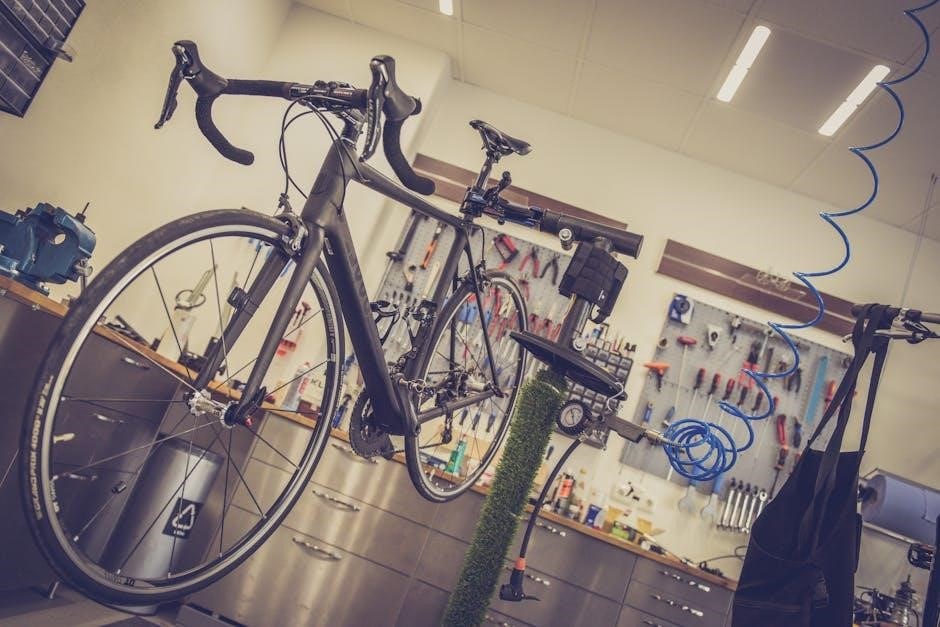

SRAM Guide RSC Brakes: A Comprehensive Guide (Updated 12/22/2025)
SRAM Guide RSC disc brakes are a popular choice, offering powerful and consistent braking. They feature SwingLink technology, tool-free adjustments, and customizable feel for precision.
The SRAM Guide RSC brakes represent a significant step forward in hydraulic disc brake technology, catering to mountain bikers and road cyclists seeking reliable performance. Released as a premium offering within the Guide series, the RSC model balances power, modulation, and adjustability. These brakes quickly gained popularity due to their enhanced features over the Guide R, including the SwingLink lever design and refined contact point control.
Today, December 22, 2025, the Guide RSC remains a top contender, known for its ability to handle demanding trails and provide consistent stopping power. Riders appreciate the customizable feel, achieved through tool-free reach and contact point adjustments. The improved cooling features, with a more open caliper design, contribute to sustained performance, even during extended descents. This guide will delve into every aspect of the Guide RSC, from installation to maintenance and upgrades.
What Makes the Guide RSC Stand Out?
The SRAM Guide RSC distinguishes itself through a combination of refined design and performance-enhancing features. Unlike the Guide R, the RSC boasts the SwingLink lever, providing a more ergonomic and powerful feel. A key differentiator is the enhanced cooling system; the caliper’s design allows for greater airflow around the pads and pistons, mitigating brake fade during prolonged use.
Furthermore, the RSC offers superior adjustability with both tool-free reach and contact point adjustments, enabling riders to fine-tune braking feel to their preference. Compatibility with various calipers, including older Guide models, adds to its versatility. Experienced riders often choose the RSC for its ability to maintain consistent performance, even under intense braking demands, and its upgrade potential.
Key Features & Technologies
SRAM Guide RSC brakes utilize SwingLink lever design, contact point adjustment, tool-free reach adjustment, and the BleedingEase system for optimal performance and customization.
SwingLink Lever Design
The SRAM Guide RSC brakes feature a unique SwingLink lever design, fundamentally changing the leverage ratio and feel. This innovative design translates into a more powerful and consistent braking experience, offering enhanced modulation and control for riders tackling diverse terrain. Unlike traditional brake levers, SwingLink moves the cam closer to the handlebar.
This strategic placement results in a more direct connection and reduced dead stroke, improving responsiveness and confidence. The SwingLink mechanism also contributes to a more ergonomic lever feel, reducing hand fatigue during extended rides. It’s a key component in the Guide RSC’s ability to deliver precise braking power with minimal effort, making it a favorite among mountain bikers and discerning cyclists.
Contact Point Adjustment
A defining feature of the SRAM Guide RSC brakes is the ability to fine-tune the contact point. This adjustment allows riders to personalize the feel of the brakes, dictating how far the lever travels before engaging the caliper. Riders can choose a firm, immediate bite or a softer, more progressive feel, catering to individual preferences and riding styles.
This customization is crucial for optimizing braking performance in various conditions. A closer contact point provides quicker engagement for technical descents, while a further contact point offers more modulation for controlled braking on longer rides. The Guide RSC’s contact point adjustment empowers riders to dial in their brakes for maximum control and confidence on the trail.
Tool-Free Reach Adjustment
The SRAM Guide RSC brakes boast a convenient tool-free reach adjustment, allowing riders to quickly and easily customize the distance between the lever and the handlebar. This feature is essential for accommodating different hand sizes and preferences, ensuring optimal comfort and control. No Allen keys or specialized tools are required – a simple dial allows for on-the-fly adjustments.

Proper reach adjustment is critical for maximizing braking power and minimizing hand fatigue. A correctly adjusted lever allows riders to engage the brakes effectively without overextending their fingers. This feature is particularly beneficial for riders who switch between bikes or wear gloves of varying thicknesses, providing a consistently comfortable and secure grip.
BleedingEase System
SRAM’s BleedingEase system, integrated into the Guide RSC brakes, significantly simplifies the often-dreaded brake bleeding process. This innovative design streamlines fluid replacement, reducing mess and complexity for both home mechanics and professional technicians. The system allows for a cleaner, more efficient bleed, minimizing air bubbles and ensuring consistent brake performance.
The BleedingEase port facilitates easy access for attaching a bleed kit, while the internal routing minimizes fluid spillage. Regular bleeding is crucial for maintaining optimal braking power, especially with frequent use and exposure to heat. The system helps maintain consistent lever feel and responsiveness, contributing to rider confidence and safety on the trails or road.

Guide RSC vs. Other Guide Models
The Guide RSC sits between the Ultimate and R, offering a balance of features and price. It shares caliper compatibility across the Guide series.
Guide RSC vs; Guide Ultimate
While the Guide RSC and Guide Ultimate share a similar foundation, key distinctions set them apart. The Ultimate is positioned as the premium offering, boasting lighter weight – more than a couple of grams lighter than the RSC – and a more refined aesthetic. However, the RSC isn’t far behind in performance.
A notable difference lies in the caliper design; the RSC’s caliper appears more chiseled. Crucially, SRAM enhanced airflow around the pads and pistons in the RSC, improving cooling and pad accessibility from the top. This design addresses heat management, a critical factor in sustained braking performance. Both models offer excellent modulation and power, but the Ultimate prioritizes weight savings, while the RSC focuses on thermal management and ease of maintenance.
Guide RSC vs. Guide R
The SRAM Guide RSC represents a step up from the Guide R, offering enhanced features and adjustability. Both brakes share a similar braking power foundation, but the RSC introduces SRAM’s SwingLink lever design and contact point adjustment, allowing riders to fine-tune brake feel for personalized control. The Guide R lacks these refinements, providing a more straightforward braking experience.
Importantly, lever swaps between the RSC and RS (found on the Guide R) are generally straightforward on current models, and even compatible with older 11 Guide calipers. Upgrading to an RSC lever on a Guide R caliper can significantly improve modulation and control. A thorough bleed and ensuring pads aren’t overly worn are crucial after any lever swap, alongside caliper pressurization.
Caliper Compatibility Across Guide Series
SRAM’s Guide series demonstrates notable caliper compatibility, allowing for upgrades and component mixing within the range. The Guide RSC caliper is fundamentally compatible with other Guide models, including the Guide R and even older 11 Guide calipers. This interchangeability opens possibilities for riders seeking to enhance braking performance without a complete system overhaul.
The RSC caliper’s design incorporates improved airflow around the pads and pistons, enhancing cooling and reducing brake fade, a benefit transferable when used with levers from other Guide models. However, ensure proper bleeding after any component swap to maintain optimal brake function. The hose banjo position on the RSC provides more space for pad removal from the top.

Installation & Setup
Proper SRAM Guide RSC brake installation involves mounting the caliper and lever, routing the hose correctly, and ensuring accurate brake pad placement for optimal performance.
Mounting the Guide RSC Caliper
Successfully mounting the SRAM Guide RSC caliper requires careful attention to detail. Ensure compatibility with your frame or fork’s mounting standard – IS or Post Mount. Utilize the correct adapter if necessary, tightening it securely to prevent movement during braking.
Position the caliper so the brake pads align with the rotor’s braking surface; avoid contact during installation. Tighten the caliper mounting bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque, preventing over or under-tightening.
The Guide RSC’s design features increased airflow around the pads, accessible from the top for easy removal. This improved cooling helps maintain consistent braking power, especially during extended descents. Double-check all connections before proceeding to the next step.
Lever Installation
Installing the SRAM Guide RSC lever is straightforward, but precision is key. Securely attach the lever to the handlebar, utilizing the tool-free reach adjustment to find a comfortable position. Ensure the clamp bolts are tightened to the recommended torque specification to prevent slippage during rides.
Connect the brake hose to the lever, ensuring a snug and secure fit. Avoid cross-threading the hose fitting. The RSC lever boasts SRAM’s SwingLink design, enhancing modulation and control.
Proper lever installation is crucial for optimal braking performance and rider confidence. Double-check all connections and adjustments before proceeding to hose routing and cutting. A correctly installed lever contributes significantly to the overall braking experience.
Hose Routing & Cutting
Proper hose routing is vital for SRAM Guide RSC brake performance, avoiding kinks and abrasion; Route the hose along the frame, utilizing frame guides and secure zip ties. Maintain sufficient slack for handlebar movement, preventing strain on the hose and fittings.
When cutting the hose, use a dedicated brake hose cutter for a clean, square cut. Avoid crushing or deforming the hose. Deburr the cut end to prevent contamination and ensure a smooth connection.
The RSC’s hose banjo position allows for increased airflow around the pads. Carefully measure and cut the hose to the appropriate length, considering the caliper and lever positions. Securely install the hose fittings, tightening to the specified torque.
Brake Pad Installation
Installing SRAM Guide RSC brake pads is straightforward, but requires cleanliness. Ensure the caliper and pistons are free from contamination. Retract the pistons fully using a brake pad spreader or a clean tool.
Align the new brake pads with the caliper mounting posts, ensuring correct orientation. Secure the pads with the retaining clips or bolts, tightening to the specified torque; Avoid touching the pad material to prevent contamination.
The Guide RSC’s caliper design offers improved airflow around the pads, aiding cooling. After installation, pump the brake lever several times to seat the pads against the rotor. Verify proper pad contact and function before riding.

Bleeding the SRAM Guide RSC Brakes
SRAM Guide RSC brakes require DOT 5.1 fluid for optimal performance. Regular bleeding eliminates air bubbles, ensuring consistent lever feel and powerful braking capabilities.
DOT 5.1 Fluid Requirements
SRAM Guide RSC brakes absolutely require DOT 5.1 brake fluid. Using any other fluid type will compromise performance and potentially damage the braking system. DOT 5.1 has a higher boiling point than DOT 4, crucial for resisting brake fade during intense riding.
Ensure the fluid is fresh and sealed, as it readily absorbs moisture from the air, reducing its effectiveness. Contaminated fluid leads to spongy lever feel and diminished braking power. Always store DOT 5.1 in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place. Never reuse old brake fluid; always discard it responsibly. Proper fluid maintenance is paramount for reliable and consistent braking performance with your SRAM Guide RSC brakes.
Bleeding Kit Options
Several options exist for bleeding SRAM Guide RSC brakes. SRAM offers its own bleed kit, specifically designed for their brakes, ensuring compatibility and optimal results. These kits typically include syringes, tubing, adapters, and mineral oil. Universal bleed kits are available, but verifying compatibility with DOT 5.1 fluid and SRAM banjo fittings is crucial.
Some riders prefer using a pressure bleeder, which forces fluid through the system, potentially simplifying the process. However, caution is advised to avoid over-pressurizing the system. Regardless of the kit chosen, ensure it’s clean and in good working order. A quality bleed kit significantly contributes to achieving a firm, consistent brake feel for your Guide RSC brakes.
Step-by-Step Bleeding Procedure
Begin by securing the bike and protecting the frame from fluid spills. Attach the bleed tubing to the caliper bleed port, ensuring a tight seal. Slowly push a small amount of DOT 5.1 fluid through the system to remove any air bubbles initially. Next, gently pump the brake lever and simultaneously open and close the bleed screw at the caliper.
Repeat this process until no more bubbles appear in the fluid. Finally, close the bleed screw and carefully remove the tubing. Pressurize the caliper after bleeding to maintain consistency. A thorough bleed ensures optimal performance and a firm, reliable brake feel for your SRAM Guide RSC brakes.
Pressurizing the Caliper After Bleeding
After a successful bleed, pressurizing the SRAM Guide RSC caliper is crucial for consistent performance. The heat generated during braking can cause fluid to vaporize, introducing air into the system. Pressurization helps minimize this. Gently push the brake pads against the rotor while the lever is held in a relaxed position.
This forces fluid into the caliper, reducing the chance of air pockets forming. It may be necessary to repeat this process several times, especially after a significant bleed or at the bike park. Regular re-pressurization maintains a firm lever feel and reliable braking power, even under demanding conditions.

Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Regularly check SRAM Guide RSC brake pad wear and rotor condition. Address brake fade and lever feel issues promptly for optimal performance and safety.
Pad Wear Indicators
SRAM Guide RSC brakes don’t feature traditional pad wear indicators like audible squealers. Instead, riders must visually inspect pad thickness regularly. As pads wear, the backing plate will become more visible. It’s crucial to replace pads before they are completely worn down to prevent rotor damage and maintain optimal braking power.
Pay attention to lever feel; a spongy or bottoming-out lever often indicates worn pads. Frequent brake checks, especially during demanding rides, are essential. Consider replacing pads in pairs for even wear and consistent performance. Ignoring pad wear can lead to reduced stopping power and potentially dangerous situations on the trail or road. Proactive maintenance ensures reliable braking.
Rotor Compatibility
SRAM Guide RSC brakes are compatible with a wide range of rotors, but optimal performance is achieved with SRAM Centerline rotors. These rotors are designed to maximize braking power and minimize noise. Riders can use third-party rotors, but ensure they are specifically designed for hydraulic disc brakes and compatible with SRAM calipers.
Rotor size selection depends on riding style and terrain. Larger rotors offer increased stopping power and heat dissipation, ideal for aggressive downhill riding. Smaller rotors are lighter and suitable for cross-country or road cycling. Always check the caliper’s maximum rotor size compatibility before upgrading. Proper rotor alignment is crucial for quiet operation and consistent braking.
Addressing Brake Fade
Brake fade, a loss of braking power due to overheating, is a common issue with hydraulic disc brakes like the SRAM Guide RSC. The Guide RSC’s improved caliper design with increased airflow helps mitigate this, but it’s not a complete solution. Long descents or repeated hard braking generate significant heat, causing brake fluid to boil and reducing effectiveness.
To combat fade, ensure proper rotor size for your riding style. Upgrading to larger rotors enhances heat dissipation. Regularly flush and replace brake fluid (DOT 5.1) as degraded fluid boils at a lower temperature. Consider using sintered brake pads, which offer higher heat tolerance. Periodically allow brakes to cool during extended descents.
Lever Feel Issues & Solutions
Several factors can contribute to inconsistent or poor lever feel in SRAM Guide RSC brakes. Air bubbles in the system are a primary culprit, resulting in a spongy feel; a thorough bleed is the solution. Degraded brake fluid also impacts performance, requiring a fluid flush. Ensure proper caliper alignment to prevent piston binding, which causes uneven pad wear and a dragging sensation.
If swapping levers (like from RS to RSC), a complete bleed is crucial to maintain consistency. Pressurizing the caliper post-bleed helps stabilize the feel. Check for hose kinks or restrictions. Regularly inspect pads for wear and contamination, as these affect modulation and power.

Upgrades & Modifications
SRAM Guide RSC brakes offer upgrade paths, including lever swaps, caliper enhancements, and hose replacements, to optimize performance and cooling for demanding riding conditions.
RSC Lever Swaps with RS Levers
Swapping SRAM Guide RSC levers with RS levers is a common and generally straightforward upgrade, particularly for riders seeking a specific feel or aesthetic. Current model Guide brakes demonstrate compatibility, allowing for seamless integration without significant complications. Experienced users have successfully performed these swaps, even extending compatibility to older 11 Guide calipers.
However, a crucial step following the lever swap is a complete brake bleed. This ensures optimal performance and consistent lever feel. Additionally, it’s recommended to pressurize the caliper after bleeding; this maintains consistency, especially during intense use like at a bike park. Frequent re-pressurization, potentially every few days, may be necessary due to heat-induced fluid degradation within the brake system. This proactive maintenance helps sustain reliable braking power.
Caliper Upgrades
While the SRAM Guide RSC caliper offers excellent performance, upgrades can further enhance braking power and heat management. The RSC caliper’s design prioritizes airflow, featuring a more open structure around the pads and pistons compared to earlier models. This improved cooling is evident in its chiseled appearance and forward hose banjo position, maximizing space for ventilation.
Upgrading to a caliper with enhanced thermal capacity can be beneficial for riders frequently encountering demanding descents. Consider options designed for increased heat dissipation. Remember that even subtle changes, like improved airflow, contribute to maintaining consistent braking performance by mitigating brake fade. Proper pad selection is also crucial when considering caliper upgrades, ensuring optimal compatibility and heat resistance.
Hose Upgrades
Upgrading the brake hose on your SRAM Guide RSC brakes can improve braking feel and consistency, particularly for riders seeking enhanced modulation or reduced brake line expansion. While the stock hoses are reliable, aftermarket options often utilize more durable materials and tighter tolerances. Braided hoses, for example, minimize expansion under pressure, resulting in a firmer, more predictable brake lever feel.
When selecting a new hose, ensure compatibility with the Guide RSC’s fittings. Consider the length needed for your bike’s configuration, and always bleed the brakes thoroughly after any hose replacement to eliminate air bubbles. Proper hose routing is also vital to prevent abrasion and maintain optimal performance. A high-quality hose contributes to a more responsive and reliable braking system.
Optimizing Cooling for Hot Conditions
SRAM Guide RSC brakes, like all hydraulic disc brakes, can experience reduced performance during extended descents due to heat buildup. The RSC’s caliper design already incorporates improved airflow around the pads and pistons, but further optimization is possible. Using larger rotors dissipates heat more effectively, delaying brake fade. Regularly inspecting and cleaning rotors prevents heat retention from embedded contaminants.
Consider using brake pads with better heat management properties. During long rides, briefly feathering the brakes allows them to cool intermittently. Proper hose routing, avoiding tight bends, also aids in heat dissipation. Remember that fluid degradation accelerates with heat, so frequent fluid changes are crucial for maintaining consistent braking power in demanding conditions.

Advanced Considerations
SRAM Guide RSC performance is impacted by heat and fluid age; regular maintenance and fluid replacement are vital for long-term reliability and optimal braking.
Impact of Heat on Brake Performance
SRAM Guide RSC brakes, like all hydraulic disc brakes, are susceptible to performance degradation under extreme heat. Prolonged and intense braking, especially during descents, generates significant heat within the system. This heat can cause the DOT 5.1 brake fluid to boil, leading to brake fade – a noticeable reduction in braking power.
The Guide RSC’s design incorporates features to mitigate this, such as increased airflow around the pads and pistons, improving cooling. However, even with these improvements, consistent heat buildup can still degrade fluid performance. The fluid starts to degrade, requiring more frequent bleeding and replacement. Regular checks and proactive maintenance are crucial for maintaining consistent braking power in demanding conditions. Re-pressurizing the caliper after bleeding can also help maintain consistency.
Fluid Replacement Schedule
Maintaining optimal performance of your SRAM Guide RSC brakes necessitates a regular fluid replacement schedule. DOT 5.1 fluid is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture over time, diminishing braking performance and increasing the risk of corrosion. A general guideline suggests replacing the fluid at least once a year, or more frequently for riders who frequently encounter demanding conditions.
Riders who frequently ride bike parks or engage in prolonged descents should consider replacing the fluid every 3-6 months, as the brakes experience significantly higher temperatures. The fluid degrades faster under heat. Regular bleeding and fluid replacement ensure consistent lever feel and maximum braking power, safeguarding your performance and safety on the trails.
Long-Term Maintenance Tips
To ensure the longevity and consistent performance of your SRAM Guide RSC brakes, implement a proactive maintenance routine. Regularly inspect brake pads for wear and replace them promptly to prevent rotor damage. Clean the calipers and rotors with isopropyl alcohol to remove contaminants that can reduce braking efficiency. Periodically check hose connections for leaks or damage, tightening as needed.
Store your bike in a cool, dry environment to minimize fluid degradation. Consider applying a corrosion inhibitor to exposed metal parts. Following these simple steps will help maintain optimal braking power and extend the lifespan of your Guide RSC brakes, providing reliable performance for years to come.
Common Issues and Their Resolutions
A frequent issue with SRAM Guide RSC brakes is lever feel inconsistency, often resolved with a thorough bleed and post-bleed caliper pressurization, especially after intense use. Brake fade, caused by overheating, can be mitigated by ensuring adequate rotor cooling and considering upgraded rotors. Air bubbles in the system lead to spongy brakes; a bleed resolves this.
If experiencing pad contamination, replace both pads and clean the rotor. For lever movement issues, check for proper installation and hose routing. Remember, DOT 5.1 fluid degrades with heat, so regular fluid replacement is crucial. Addressing these common problems ensures continued reliable braking performance.